Wonderful Pomegranate Tree
The Wonderful Pomegranate is a captivating fruit-bearing tree with brilliant crimson blossoms and deep-red, jewel-like arils. This versatile tree, known for its sweet-tart fruit, adds both visual appeal and flavor to gardens and orchards.
Not compatible with your zone (2a)
General Plant Information
Wonderful Pomegranate Tree
The Wonderful Pomegranate Tree, Punica granatum ‘Wonderful,’ is a captivating addition to any garden or orchard. Cultivate the Wonderful Pomegranate Tree (Punica granatum ‘Wonderful’) in your garden for a blend of beauty and utility. Boasting striking crimson flowers, glossy leaves, and delicious, antioxidant-rich fruit, this tree is a multifaceted gem. Discover its ornamental value, culinary potential, and rich historical significance.
Fruit Description:
This beautiful tree produces remarkable fruits. These large, spherical wonders feature tough, deep-red skin that encases the real treasure—juicy, sweet-tart arils. These arils are not only delightful to the taste buds but also rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
Tree Description:
The Wonderful Pomegranate tree is an aesthetic delight. It boasts vibrant crimson flowers with waxy petals, dark green leaves that form an attractive canopy, and a sturdy root system. Moreover, it’s smooth, gray bark adds to its overall appeal, making it an excellent choice for both aesthetic and practical purposes.
Uses:
This versatile tree offers numerous uses. It’s a visual delight, enhancing gardens and landscapes with its ornate beauty. Moreover, the arils of this pomegranate tree, additionally offers a blast of flavor and a touch of elegance to a variety of gourmet dishes, are also a source of rich, healthy juice.
History:
The Wonderful Pomegranate tree has a rich history, dating back to ancient times. Therefore, it’s revered for its symbolism and cultural significance, it has made appearances in art, literature, and traditional practices. Furthermore, its timeless allure continues to captivate gardeners, chefs, and enthusiasts alike.
Size and Spacing:
To maximize the potential of your Pomegranate Tree, proper spacing and size considerations are crucial. In addition, to ensure adequate spacing of 12 to 16 feet between trees to allow for growth and air circulation, and maintain an ideal height of 12 to 16 feet. Prune regularly to maintain shape and size.
Mature Size and Form
Plant most fruit trees about 10 – 15 feet apart. Some varieties like Figs, Pomegranates, and Mulberries can grow larger quickly.
Planning is the most important step when planting a tree. Plant your tree where it has enough space to grow to its full potential. Otherwise, your tree will grow into your surrounding trees. A tree that can grow taller with faster growth will overshadow nearby trees. You may need to move other trees to allow for the one that is thriving rather than cutting back one that naturally grows fast and tall.
Additional Information
Plant Type: DeciduousUSDA Hardiness Zones: 7-12
Pollination: Self-Fruitful / Self Pollinating
Planting Information
Soil and Planting: Plant in soil that drains well. Dig a hole that is as deep as the tree’s roots and at least twice as wide.
Place the tree in the hole and backfill around the plant’s roots with a mixture of the native soil and high-quality planting mix that has washed sand and organic fertilizer.
Create a basin around the roots drip zone so that water collects. Water deeply until the roots and nearby soil is saturated and reaches field capacity.
Plant Care Information
How To Water - Frequency and Duration to Irrigate
Irrigation Water Quantity and frequency based on tree maturity – Fully saturate the soil with water once per week during the early spring. Increase to twice per week as the weather warms. Water 3 times per week or more during hot summers. Provide about 5 gallons of water for a 5 gallons size plant, 15 gallons of water for a #15 size container plant, and 25 gallons for a #25 depending on soil type. Sandy soils can hold less water required more frequently, while clay soils can hold more water and require less frequent irrigation. Young trees with less developed roots require water more frequently while mature plants with developed roots will require less frequent watering.
Fertilizer and Plant Nutrition
Fertilize your tree every 3-4 months. Use a complete balance fertilizer with a 1-1-1 or 2-1-1 NPK ratio during the Spring and Summer growing season, and a formula with more phosphorus and potassium before the tree flowers to improve fruit production and development.
Winter Pruning and Summer Thinning
Prune your tree to allow light into its center for proper growth and fruit production.
Prune fruit trees in the Winter to maintain size and shape to prepare for Spring growth. Thin the tree in the Summer, and remove excessive fruits. Remove any dry twigs and branches. Cut off any new growth below the graft or very low in the tree, this will direct the plant’s energy to its main branches. Thin your trees during the Spring and Summer seasons to ensure the plant’s energy is directed as desired. Harvest ripe fruit to prevent undesired pests.
Harvesting and Pest Management
The basics of integrated pest management is cleanliness and the use of a combination of methods. This means we use an organic pesticide when the pest population reaches a threshold that requires action. Horticultural oils such as Neem oil is an organic pesticide that controls tiny, soft bodied insects. Use organic Bordeaux and Liqui-cop to manage fungus causing diseases such as powdery mildew, rust, and leaf-curls.
Keep a clean environment, free of weeds and dropped fruit that host insects or attract animals. Harvest when fruit reaches size and store indoors. Use repellants and bird netting to protect your harvest from other animals.
Sun Exposure: Full Sun
Deciduous trees need about 5 hours of direct sunlight for proper growth and fruit production.
Sunlight Sensitive plants like Cherries, Persimmons, and Plums can burn in hot climates if they lack water. Use afternoon shade to prevent this damage. A lack of light will stunt growth; balance is key.
Limited Guarantee and Returns
Compatibility
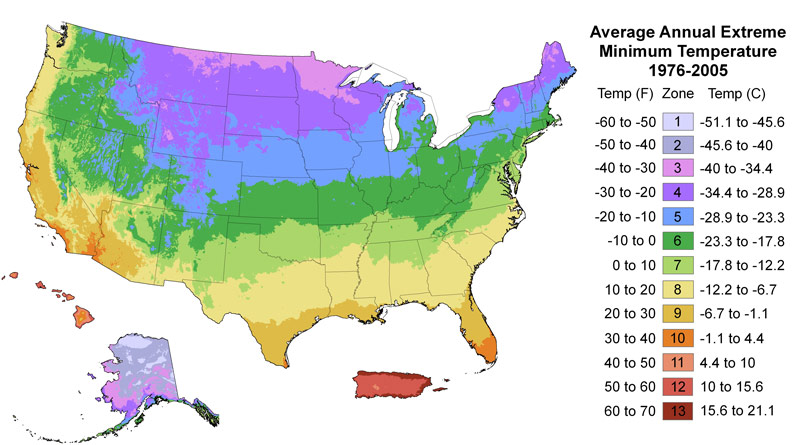
The two factors that determine if a deciduous fruit trees will grow well and produce fruit in a certain area are the Chill Hour Requirement and the Cold Hardiness. “Chill hours” are the amount of cold a deciduous fruit tree need to produce fruit. This is measured in the number of hours below 45 degrees Fahrenheit a plant must experience during its winter dormancy. Paradise Nursery only grows Low Chill fruit trees that meet the chill requirements of all areas of the United States.
The second factor is Cold Hardiness. Cold Hardiness refers to the minimum temperature a plant can tolerate. The USDA’s Cold Hardiness Zones indicate the average minimum winter temperatures of areas. Based on the shipping zipcode, our website will only allow you to add plants to your cart that grow within your USDA Hardiness Zone, and tolerate your climate.
Pollination & Propagation
(Grafting/Cutting) Most of Paradise Nursery’s edible plants are self-fruitful. Self-pollinating trees do not require an additional tree to produce fruit. For your convenience, we have indicated which trees require a pollinator, and their associated pollinators. Only the sweet cherries, avocados, and some plums require a pollinator. All of our other propagated edible plants do not require a pollinator. All of our edible plants are either grown from cuttings, budded, or grafted. This way, we can ensure that our plants are high quality and fruit immediately. Plants will generally begin fruiting within a year of planting.